

Cloud computing is the delivery of on-demand computing services over the internet. It includes storage, servers, databases, software, and more. Cloud computing enables organizations to access and use resources without the need for significant upfront investment in hardware and infrastructure.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of on-demand computing services, such as storage, servers, databases, software, and more, over the internet. It allows organizations to access and use resources without the need for significant upfront investment in hardware and infrastructure. Cloud computing enables scalability, agility, and cost efficiency, and has become a popular choice for businesses and individuals alike.
Architecture of Cloud Computing
The architecture of cloud computing refers to the overall design and structure of the various components and services that make up a cloud computing environment.
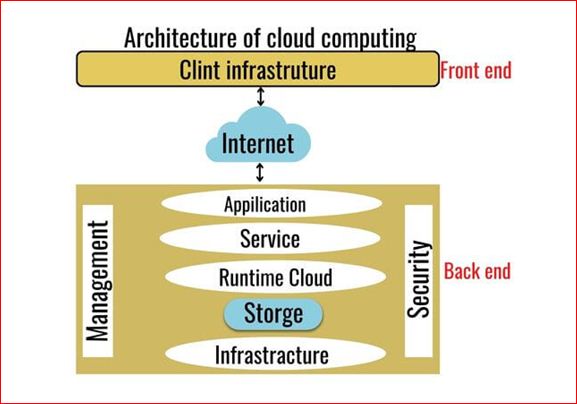
The Architecture of Cloud Computing is separated into two main aspects.
They are:
Front End
Back End
Front End
The frontend architecture of cloud computing enables users to access and interact with cloud resources and services through a user-friendly interface, such as a web browser or mobile app, providing easy and efficient management of cloud resources, monitoring of performance and usage, and access to data and applications from anywhere, at any time, with high availability and scalability.
Back End
The backend architecture of cloud computing typically includes several layers of components, including:
Application Layer: This layer consists of the applications that run on the cloud infrastructure and are accessed by users. Applications may be developed by third-party providers or built in-house.
Service Layer: This layer includes the various services offered by cloud providers, such as storage, computing power, and data processing.
Cloud runtime layer: The cloud runtime layer provides an environment for running applications and services in the cloud, enabling scalability, agility, and cost savings for cloud users.
Storage layer: The storage layer in cloud computing provides services for data storage, management, and access with high scalability and durability for cloud users.
Infrastructure Layer: This layer includes the physical hardware, such as servers, storage, and networking equipment, that provides the foundation for cloud computing.
Management: This layer provides tools for managing and monitoring cloud resources, including resource allocation, capacity planning, and performance monitoring.
Security: The security layer provides critical services, such as encryption, access control, and threat detection, to protect cloud resources and data from unauthorized access and cyber attacks.
The backend architecture of cloud computing is designed to provide scalable, reliable, and secure services to users, while also optimizing resource utilization and performance. The use of virtualization and automation enables cloud providers to offer flexible, on-demand services that can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing user needs.
Features of Cloud Computing
The features of Cloud Computing:
On-demand self-service: Users can easily access computing resources, such as servers and storage, without needing to go through a lengthy procurement process.
Broad network access: Cloud resources are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
Resource pooling: Cloud providers can pool computing resources to serve multiple users, allowing for greater efficiency and cost savings.
Rapid elasticity: Cloud resources can be quickly and easily scaled up or down as needed.
Measured service: Cloud providers can measure resource usage and bill users accordingly, allowing for more accurate and flexible pricing.
Resiliency and fault tolerance: Cloud providers typically have multiple data centers and redundancy built in to ensure high availability and minimize downtime.
Security: Cloud providers offer various security measures to protect data and applications, including firewalls, encryption, and access controls.
These features make cloud computing a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solution for a wide range of computing needs, from personal file storage to enterprise-scale application hosting.
How does Cloud Computing Works?
Cloud computing works by providing on-demand access to shared computing resources over the internet.
Cloud providers operate data centre’s with large numbers of servers, storage devices, and networking equipment that can be shared by multiple customers. Users can access these resources through a variety of interfaces, such as web browsers, APIs, or command-line interfaces.
Cloud computing typically uses a pay-per-use or subscription-based model, allowing users to scale up or down their usage of computing resources as needed, and only pay for what they use.
Cloud computing also offers various deployment models, including public, private, and hybrid clouds, allowing organizations to choose the level of control and customization they need for their computing environments.
In summary, cloud computing works by providing a flexible and scalable way to access computing resources and services over the internet, enabling users to focus on their core business and reduce the costs and complexity of managing their own IT infrastructure.

Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers several benefits that make it an attractive option for businesses and individuals, including:
Scalability: Cloud services can be scaled up or down as needed, providing flexibility and cost savings.
Cost Efficiency: Cloud computing eliminates the need for significant upfront investment in hardware and infrastructure, as users only pay for what they use.
Accessibility: Cloud services can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, making it easy to work remotely.
Reliability: Cloud providers typically offer high availability and uptime, ensuring that services are always accessible.
Security: Cloud providers typically have robust security measures in place, protecting data from unauthorized access, theft, or loss.
These benefits make cloud computing an attractive option for organizations looking to improve their efficiency, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
Challenges of Cloud computing
Some of the challenges of cloud computing include:
Security: Protecting cloud resources and data from unauthorized access, cyber attacks, and data breaches.
Data Privacy: Ensuring that sensitive data is protected and meets regulatory requirements.
Availability: Ensuring that cloud resources are available and accessible to users, even during peak usage periods.
Performance: Ensuring that cloud services perform well, with low latency and high throughput, to meet user expectations.
Vendor Lock-in: Avoiding the risk of being tied to a single cloud provider, and the potential for increased costs and limited flexibility.
Interoperability: Ensuring that cloud services and applications can work together seamlessly, regardless of the cloud provider or technology used.
Cost Management: Managing cloud costs effectively, and avoiding unexpected expenses, through efficient resource allocation and monitoring.
Governance and Compliance: Ensuring that cloud resources and services comply with regulatory requirements and internal policies, and managing risks associated with third-party providers.
Skills Gap: Addressing the shortage of skilled professionals who can manage and optimize cloud resources and services effectively.
Migration: Planning and executing the migration of existing applications and data to the cloud, while minimizing disruption and ensuring compatibility.
